polarimeter optical isomers|how to draw optical isomers : chain store The stereoisomer that is optical active is also called as optical isomer. Chiral compound is optical active. Achiral compound is optical inactive. . Figure 5.4c Measurement of Optical Rotation with Polarimeter. Since the . Resultado da 2 dias atrás · Ostend 7 day weather forecast including weather warnings, temperature, rain, wind, visibility, humidity and UV
{plog:ftitle_list}
23 de jun. de 2021 · Main info about bonus at Crystal Slots casino; 🍁 Crystal Slots .
types of optical isomers
When light is shot through a polarimeter, optical isomers can rotate the light so it comes out in with a different polarization on the other end. Armed with the knowledge of symmetry and mirror images, optical isomers should not be very difficult.
A polarimeter is an instrument used to determine the angle through which plane-polarized light has been rotated by a given sample. You will have the opportunity to use a polarimeter in the .
The stereoisomer that is optical active is also called as optical isomer. Chiral compound is optical active. Achiral compound is optical inactive. . Figure 5.4c Measurement of Optical Rotation with Polarimeter. Since the . When light is shot through a polarimeter, optical isomers can rotate the light so it comes out in a different direction on the other end. Armed with the knowledge of symmetry and mirror images, optical isomers should not be .
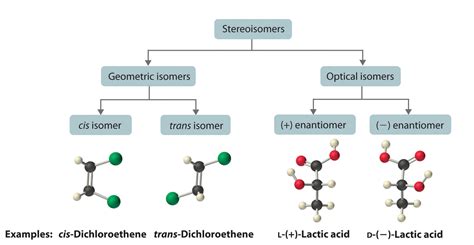
Optically active substances. An optically active substance is one which can rotate the plane of polarisation of plane polarised light. if you shine a beam of polarised monochromatic light (light of only a single frequency - in other words .The polarimeter is an instrument that measures the direction and angles of rotation of plane-polarized light. The plane-polarized light passes through the sample tube containing the solution of a sample, and the angle of rotations will be received and recorded by the analyzer, as summarized in Fig. 5.4c.. Figure 5.4c Measurement of Optical Rotation with PolarimeterFigure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Operating principle of an optical polarimeter. 1. Light source 2. Unpolarized light 3. Linear polarizer 4. Linearly polarized light 5. Sample tube containing molecules under study 6. Optical rotation due to molecules 7. . (this isomer may be referred to as (–)-lactic acid or l-lactic acid) A 50:50 mixture of .Topic 5 – Stereochemistry and optical isomers Isomerism Recap Classification of isomers Stereoisomers - enantiomers Chiral molecules (optical isomers) . Polarimeter: when plane polarised light is passed through a solution of one pure enantiomer of a compound, .
optical isomers vs stereoisomers
When light is shot through a polarimeter, optical isomers can rotate the light so it comes out in with a different polarization on the other end. Armed with the knowledge of symmetry and mirror images, optical isomers should not be very difficult. There are two ways optical isomers can be determined: using mirror images or using planes of symmetry. Optical isomers also have no axis of symmetry, which means that there is no line that bisects the compound such that the left half is a mirror image of the right half. . Optical activity is measured by a polarimeter, and is dependent on several factors: concentration of the sample, temperature, length of the sample tube or cell, and . Plane polarized light will rotate in different directions when passing through different stereo isomers (from a pair of enantiomers). A polarimter measures .
Optical isomerism. Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same structural formula but have the atoms arranged differently in space There are two types of stereoisomerism. Geometrical (E/Z) Optical; A carbon atom that has four different atoms or groups of atoms attached to it is called a chiral carbon or chiral centre. Chira comes from a Greek word . When light is shot through a polarimeter, optical isomers can rotate the light so it comes out in with a different polarization on the other end. Armed with the knowledge of symmetry and mirror images, optical isomers should not be very difficult. There are two ways optical isomers can be determined: using mirror images or using planes of symmetry. When light is shot through a polarimeter, optical isomers can rotate the light so it comes out in a different direction on the other end. Armed with the knowledge of symmetry and mirror images, optical isomers should not be very difficult. There are two ways optical isomers can be determined: using mirror images or using planes of symmetry.
When light is shot through a polarimeter, optical isomers can rotate the light so it comes out in a different direction on the other end. Armed with the knowledge of symmetry and mirror images, optical isomers should not be very difficult. There are two ways optical isomers can be determined: using mirror images or using planes of symmetry.
It is measured using a polarimeter. An optical isomer may rotate plane polarised light in a clockwise manner (+) or in an anticlockwise manner (-). The isomers are said to be dextrorotatory (rotate to the right) and Laevorotatory (cause rotation to the left). There is no way of knowing how a specific optical isomer will affect plane polarised .When light is shot through a polarimeter, optical isomers can rotate the light so it comes out in a different direction on the other end. Armed with the knowledge of symmetry and mirror images, optical isomers should not be very difficult. . A 50:50 mixture of enantiomers has no observable optical activity. Such mixtures are called racemates or racemic modifications, and are designated (±). When chiral compounds are created from achiral compounds, the products are racemic unless a single enantiomer of a chiral co-reactant or catalyst is involved in the reaction.
It is also known as optical isomerism, as chiral compounds rotate plane-polarised light. The Polarimeter The polarimeter is a device used to measure the optical activity of organic compounds. To measure the rotation of light by a compound, the polarimeter is first aligned so that its two polarising filters Lecture 3 Lecture notes Page 1When light is shot through a polarimeter, optical isomers can rotate the light so it comes out in a different direction on the other end. Armed with the knowledge of symmetry and mirror images, optical isomers should not be very difficult. There are two ways optical isomers can be determined: using mirror images or using planes of symmetry.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.The instrument used to measure optical activity is called a polarimeter. A polarimeter is an instrument that allows polarized light to travel through a sample tube containing an organic compound and the degree to which an organic compound rotates plane-polarized light is measured. . For the examples below, both compounds are S-isomer, .
Optical isomers, or enantiomers, are molecules that are made up of identical atoms, bonded together in the same way, i.e. they have the same connectivity. . It is possible to build your own polarimeter, quite easily in the class room, or even at home, to detect the ‘optical activity. of chiral molecules: The experiment. A pdf version of .
optical isomers vs enantiomers
Specific Rotation— The reference Specific rotation 781S in a monograph signifies that specific rotation is to be calculated from observed optical rotations in the Test solution obtained as directed therein. Unless otherwise directed, measurements of optical rotation are made at 589 nm at 25.Where a photoelectric polarimeter is used, a single measurement, corrected for the .When molecules capable of exhibiting optical isomerism are obtained from natural sources, they usually consist of one of the possible isomers (one of the enantiomers) and on extraction, purification and isolation, they show optical activity (that is rotating the plane of polarised light in a polarimeter tube). This is due to the need for .The plane of polarization can be determined by an instrument called a polarimeter, shown in the diagram below. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Operating principle of an optical polarimeter. 1. Light source 2. Unpolarized light 3. Linear polarizer 4. Linearly polarized light 5. Sample tube containing molecules under study 6. Optical rotation due to .Optical isomerism is a case where the isomers display identical characteristics in terms of molecular weight as well as chemical and physical properties. However, they differ in their effect on the rotation of polarized light.
Optical rotation, also known as polarization rotation or circular birefringence, is the rotation of the orientation of the plane of polarization about the optical axis of linearly polarized light as it travels through certain materials. Circular birefringence and circular dichroism are the manifestations of optical activity.Optical activity occurs only in chiral materials, those lacking .When light is shot through a polarimeter, optical isomers can rotate the light so it comes out in with a different polarization on the other end. Armed with the knowledge of symmetry and mirror images, optical isomers should not be very difficult. There are two ways optical isomers can be determined: using mirror images or using planes of symmetry.
optical isomers enantiomers
wilson rockwell hardness tester series 2000
Preços de instalar ou trocar box de acrílico em Manaus. Serviços relacionados a instalação ou troca de box de acrílico. Preço. Troca de dobradiças de box de acrílico. R$ 160. Troca de roldana de box de acrílico. R$ 190. .
polarimeter optical isomers|how to draw optical isomers